Which Measure Of Central Tendency Is Most Often Used When The Data Has Extreme Scores?
Statistical significance is a term used past researchers to land that it is unlikely their observations could have occurred nether the nothing hypothesis of a statistical test. Significance is usually denoted by a p-value, or probability value.
Statistical significance is capricious – it depends on the threshold, or blastoff value, chosen by the researcher. The most mutual threshold is p < 0.05, which ways that the data is likely to occur less than v% of the time nether the null hypothesis.
When the p-value falls beneath the called alpha value, and so we say the issue of the test is statistically significant.
Your choice of t-test depends on whether y'all are studying 1 group or ii groups, and whether you care about the direction of the difference in group ways.
If you lot are studying ane group, use a paired t-test to compare the group mean over time or afterwards an intervention, or utilize a one-sample t-test to compare the group hateful to a standard value. If you are studying ii groups, use a two-sample t-examination.
If you lot want to know only whether a difference exists, use a 2-tailed test. If you want to know if one group hateful is greater or less than the other, apply a left-tailed or right-tailed i-tailed examination.
A t-exam measures the difference in group ways divided by the pooled standard fault of the two group means.
In this mode, it calculates a number (the t-value) illustrating the magnitude of the difference between the ii grouping ways being compared, and estimates the likelihood that this difference exists purely by take chances (p-value).
A one-sample t-test is used to compare a single population to a standard value (for example, to determine whether the average lifespan of a specific boondocks is different from the land boilerplate).
A paired t-examination is used to compare a unmarried population before and after some experimental intervention or at two different points in time (for instance, measuring student performance on a test before and after existence taught the material).
A regression model is a statistical model that estimates the human relationship between ane dependent variable and one or more independent variables using a line (or a plane in the case of two or more than independent variables).
A regression model can be used when the dependent variable is quantitative, except in the case of logistic regression, where the dependent variable is binary.
Simple linear regression is a regression model that estimates the relationship betwixt one independent variable and one dependent variable using a straight line. Both variables should be quantitative.
For instance, the relationship between temperature and the expansion of mercury in a thermometer can be modeled using a straight line: equally temperature increases, the mercury expands. This linear relationship is and then certain that we can use mercury thermometers to measure temperature.
Linear regression near oft uses hateful-foursquare fault (MSE) to calculate the error of the model. MSE is calculated by:
- measuring the distance of the observed y-values from the predicted y-values at each value of x;
- squaring each of these distances;
- calculating the hateful of each of the squared distances.
Linear regression fits a line to the data by finding the regression coefficient that results in the smallest MSE.
The merely difference between one-fashion and two-way ANOVA is the number of independent variables. A one-way ANOVA has one contained variable, while a two-way ANOVA has two.
- One-way ANOVA: Testing the human relationship between shoe brand (Nike, Adidas, Saucony, Hoka) and race stop times in a marathon.
- Two-mode ANOVA: Testing the relationship betwixt shoe brand (Nike, Adidas, Saucony, Hoka), runner historic period group (inferior, senior, main'south), and race finishing times in a marathon.
All ANOVAs are designed to test for differences amidst iii or more than groups. If yous are only testing for a difference between two groups, use a t-test instead.
In ANOVA, the null hypothesis is that there is no difference amid grouping means. If any grouping differs significantly from the overall grouping mean, then the ANOVA will report a statistically pregnant outcome.
Significant differences among group means are calculated using the F statistic, which is the ratio of the mean sum of squares (the variance explained past the contained variable) to the hateful foursquare error (the variance left over).
If the F statistic is higher than the critical value (the value of F that corresponds with your alpha value, ordinarily 0.05), then the divergence among groups is deemed statistically significant.
A factorial ANOVA is whatever ANOVA that uses more than ane chiselled contained variable. A two-fashion ANOVA is a blazon of factorial ANOVA.
Some examples of factorial ANOVAs include:
- Testing the combined effects of vaccination (vaccinated or not vaccinated) and health condition (healthy or pre-existing condition) on the rate of flu infection in a population.
- Testing the effects of marital status (married, single, divorced, widowed), job condition (employed, cocky-employed, unemployed, retired), and family history (no family unit history, some family history) on the incidence of low in a population.
- Testing the effects of feed blazon (type A, B, or C) and barn crowding (not crowded, somewhat crowded, very crowded) on the final weight of chickens in a commercial farming performance.
The Akaike data benchmark is calculated from the maximum log-likelihood of the model and the number of parameters (Grand) used to attain that likelihood. The AIC function is 2K – 2(log-likelihood).
Lower AIC values indicate a better-fit model, and a model with a delta-AIC (the difference between the 2 AIC values being compared) of more than -2 is considered significantly improve than the model it is being compared to.
In statistics, model selection is a process researchers apply to compare the relative value of unlike statistical models and determine which one is the all-time fit for the observed information.
The Akaike data criterion is ane of the most common methods of model selection. AIC weights the power of the model to predict the observed information against the number of parameters the model requires to reach that level of precision.
AIC model choice can assistance researchers find a model that explains the observed variation in their data while avoiding overfitting.
The test statistic will modify based on the number of observations in your data, how variable your observations are, and how strong the underlying patterns in the data are.
For example, if one data set has higher variability while some other has lower variability, the outset information set up will produce a test statistic closer to the null hypothesis, fifty-fifty if the true correlation between 2 variables is the same in either information fix.
P-values are normally automatically calculated by the program you use to perform your statistical test. They can also exist estimated using p-value tables for the relevant test statistic.
P-values are calculated from the null distribution of the exam statistic. They tell y'all how often a exam statistic is expected to occur under the naught hypothesis of the statistical test, based on where information technology falls in the null distribution.
If the examination statistic is far from the mean of the null distribution, and then the p-value will be small, showing that the examination statistic is non probable to have occurred nether the null hypothesis.
The alpha value, or the threshold for statistical significance, is arbitrary – which value you apply depends on your field of study.
In about cases, researchers apply an alpha of 0.05, which means that at that place is a less than 5% chance that the information being tested could have occurred under the null hypothesis.
Some variables have stock-still levels. For example, gender and ethnicity are e'er nominal level information considering they cannot be ranked.
All the same, for other variables, you tin can choose the level of measurement. For example, income is a variable that can be recorded on an ordinal or a ratio scale:
- At an ordinal level, you could create v income groupings and lawmaking the incomes that fall within them from ane–5.
- At a ratio level, you would record exact numbers for income.
If you accept a choice, the ratio level is always preferable because you can analyze data in more than ways. The higher the level of measurement, the more precise your data is.
Nominal data is data that can be labelled or classified into mutually exclusive categories inside a variable. These categories cannot exist ordered in a meaningful fashion.
For instance, for the nominal variable of preferred mode of transportation, you may take the categories of car, omnibus, train, tram or cycle.
The conviction level is the pct of times you expect to get close to the same estimate if you run your experiment again or resample the population in the same style.
The conviction interval consists of the upper and lower bounds of the estimate y'all wait to find at a given level of conviction.
For instance, if yous are estimating a 95% confidence interval around the mean proportion of female person babies built-in every twelvemonth based on a random sample of babies, you might find an upper bound of 0.56 and a lower spring of 0.48. These are the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval. The conviction level is 95%.
This means that 95% of the calculated conviction intervals (for this sample) contains the true hateful of the population.
The z-score and t-score (aka z-value and t-value) bear witness how many standard deviations away from the mean of the distribution you are, assuming your data follow a z-distribution or a t-distribution.
These scores are used in statistical tests to show how far from the mean of the predicted distribution your statistical estimate is. If your test produces a z-score of two.5, this means that your estimate is two.v standard deviations from the predicted mean.
The predicted hateful and distribution of your estimate are generated by the cypher hypothesis of the statistical test you are using. The more standard deviations abroad from the predicted mean your approximate is, the less likely it is that the approximate could have occurred under the null hypothesis.
If your conviction interval for a difference between groups includes null, that ways that if you run your experiment again you have a skilful chance of finding no departure between groups.
If your confidence interval for a correlation or regression includes nix, that means that if you run your experiment again there is a skilful chance of finding no correlation in your data.
In both of these cases, y'all will too observe a high p-value when you lot run your statistical test, pregnant that your results could accept occurred under the goose egg hypothesis of no relationship between variables or no difference between groups.
Ordinal data has ii characteristics:
- The information can be classified into different categories within a variable.
- The categories accept a natural ranked order.
However, unlike with interval information, the distances between the categories are uneven or unknown.
The t-distribution is a mode of describing a prepare of observations where about observations autumn close to the mean, and the rest of the observations make up the tails on either side. It is a type of normal distribution used for smaller sample sizes, where the variance in the information is unknown.
The t-distribution forms a bong bend when plotted on a graph. It tin exist described mathematically using the mean and the standard difference.
A t-score (a.grand.a. a t-value) is equivalent to the number of standard deviations away from the mean of the t-distribution.
The t-score is the exam statistic used in t-tests and regression tests. It can too be used to draw how far from the hateful an observation is when the data follow a t-distribution.
A critical value is the value of the test statistic which defines the upper and lower bounds of a confidence interval, or which defines the threshold of statistical significance in a statistical test. Information technology describes how far from the mean of the distribution yous accept to become to encompass a certain corporeality of the total variation in the data (i.due east. 90%, 95%, 99%).
If y'all are amalgam a 95% confidence interval and are using a threshold of statistical significance of p = 0.05, and then your disquisitional value will exist identical in both cases.
While interval and ratio information can both be categorized, ranked, and have equal spacing between adjacent values, only ratio scales have a true zero.
For example, temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit is at an interval scale considering zero is not the lowest possible temperature. In the Kelvin calibration, a ratio scale, zero represents a total lack of thermal free energy.
Variability tells y'all how far apart points lie from each other and from the center of a distribution or a data set up.
Variability is also referred to every bit spread, scatter or dispersion.
The standard deviation is the average corporeality of variability in your information set. It tells you, on boilerplate, how far each score lies from the hateful.
In normal distributions, a high standard deviation ways that values are generally far from the hateful, while a depression standard difference indicates that values are amassed shut to the mean.
The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where most of the values lie in a normal distribution:
- Effectually 68% of values are inside ane standard deviation of the mean.
- Around 95% of values are within 2 standard deviations of the mean.
- Around 99.seven% of values are within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
The empirical rule is a quick way to go an overview of your data and cheque for any outliers or extreme values that don't follow this pattern.
Homoscedasticity, or homogeneity of variances, is an assumption of equal or similar variances in different groups existence compared.
This is an important assumption of parametric statistical tests because they are sensitive to any dissimilarities. Uneven variances in samples result in biased and skewed exam results.
The two near mutual methods for calculating interquartile range are the exclusive and inclusive methods.
The sectional method excludes the median when identifying Q1 and Q3, while the inclusive method includes the median as a value in the data ready in identifying the quartiles.
For each of these methods, yous'll need dissimilar procedures for finding the median, Q1 and Q3 depending on whether your sample size is fifty-fifty- or odd-numbered. The exclusive method works best for even-numbered sample sizes, while the inclusive method is often used with odd-numbered sample sizes.
To observe the mode:
- If your data is numerical or quantitative, order the values from low to high.
- If it is categorical, sort the values by group, in any order.
So you simply need to place the most ofttimes occurring value.
A information prepare can oft have no fashion, i manner or more than than one fashion – it all depends on how many unlike values repeat nigh frequently.
Your data can be:
- without any mode
- unimodal, with one way,
- bimodal, with two modes,
- trimodal, with three modes, or
- multimodal, with four or more modes.
The median is the near informative measure of central trend for skewed distributions or distributions with outliers. For case, the median is often used as a measure of central tendency for income distributions, which are generally highly skewed.
Because the median only uses one or two values, it'due south unaffected by extreme outliers or non-symmetric distributions of scores. In dissimilarity, the mean and manner tin vary in skewed distributions.
You lot tin discover the mean, or average, of a data set in two simple steps:
- Find the sum of the values by adding them all up.
- Divide the sum by the number of values in the data set.
This method is the aforementioned whether you are dealing with sample or population data or positive or negative numbers.
The arithmetic mean is the most unremarkably used mean. It's often just chosen the mean or the average. But there are some other types of means you can calculate depending on your research purposes:
- Weighted hateful: some values contribute more than to the mean than others.
- Geometric mean: values are multiplied rather than summed up.
- Harmonic mean: reciprocals of values are used instead of the values themselves.
To figure out whether a given number is a parameter or a statistic, ask yourself the following:
- Does the number describe a whole, consummate population where every member can be reached for data collection?
- Is it possible to collect information for this number from every fellow member of the population in a reasonable time frame?
If the answer is yep to both questions, the number is probable to be a parameter. For minor populations, data can exist collected from the whole population and summarized in parameters.
If the answer is no to either of the questions, then the number is more probable to be a statistic.
The standard fault of the mean, or simply standard error, indicates how different the population hateful is likely to be from a sample hateful. Information technology tells you how much the sample mean would vary if yous were to repeat a study using new samples from within a single population.
Effect size tells you how meaningful the human relationship between variables or the deviation between groups is.
A large effect size means that a research finding has practical significance, while a small effect size indicates express practical applications.
At that place are dozens of measures of consequence sizes. The most mutual effect sizes are Cohen's d and Pearson's r. Cohen's d measures the size of the difference between 2 groups while Pearson's r measures the forcefulness of the relationship between two variables.
In statistics, power refers to the likelihood of a hypothesis examination detecting a truthful effect if at that place is one. A statistically powerful test is more likely to reject a false negative (a Type 2 error).
If you don't ensure enough power in your study, yous may not be able to detect a statistically significant result fifty-fifty when it has practical significance. Your written report might non have the ability to answer your inquiry question.
The risk of making a Type I mistake is the significance level (or blastoff) that y'all choose. That's a value that you lot set at the beginning of your study to assess the statistical probability of obtaining your results (p value).
The significance level is ordinarily gear up at 0.05 or five%. This ways that your results merely take a 5% chance of occurring, or less, if the null hypothesis is actually true.
To reduce the Blazon I mistake probability, y'all can gear up a lower significance level.
A ability analysis is a adding that helps you decide a minimum sample size for your study. It's fabricated upward of four main components. If you know or take estimates for any three of these, y'all can calculate the 4th component.
- Statistical power: the likelihood that a test will detect an effect of a sure size if at that place is one, usually set at 80% or college.
- Sample size: the minimum number of observations needed to observe an effect of a certain size with a given ability level.
- Significance level (alpha): the maximum adventure of rejecting a true null hypothesis that you lot are willing to take, usually set at five%.
- Expected effect size: a standardized way of expressing the magnitude of the expected result of your report, commonly based on similar studies or a pilot study.
In that location are various ways to amend ability:
- Increment the potential effect size by manipulating your contained variable more than strongly,
- Increase sample size,
- Increase the significance level (alpha),
- Reduce measurement error by increasing the precision and accuracy of your measurement devices and procedures,
- Use a i-tailed exam instead of a two-tailed test for t tests and z tests.
Correlation coefficients always range between -1 and 1.
The sign of the coefficient tells y'all the management of the human relationship: a positive value means the variables change together in the same direction, while a negative value means they modify together in opposite directions.
The absolute value of a number is equal to the number without its sign. The absolute value of a correlation coefficient tells you the magnitude of the correlation: the greater the absolute value, the stronger the correlation.
You can choose from 4 main ways to detect outliers:
- Sorting your values from low to loftier and checking minimum and maximum values
- Visualizing your data with a box plot and looking for outliers
- Using the interquartile range to create fences for your data
- Using statistical procedures to identify farthermost values
Outliers are extreme values that differ from most values in the dataset. You find outliers at the extreme ends of your dataset.
The arithmetic mean is the near ordinarily used blazon of hateful and is often referred to simply as "the mean." While the arithmetic mean is based on adding and dividing values, the geometric hateful multiplies and finds the root of values.
Even though the geometric mean is a less mutual measure of central tendency, information technology's more than authentic than the arithmetic mean for percentage change and positively skewed data. The geometric mean is often reported for financial indices and population growth rates.
There are two steps to computing the geometric hateful:
- Multiply all values together to go their product.
- Detect the due northth root of the product (n is the number of values).
Before calculating the geometric hateful, note that:
- The geometric mean can only be institute for positive values.
- If any value in the data fix is zero, the geometric mean is zero.
To tidy up your missing data, your options commonly include accepting, removing, or recreating the missing information.
- Acceptance: You lot leave your information as is
- Listwise or pairwise deletion: Yous delete all cases (participants) with missing data from analyses
- Imputation: You use other information to fill in the missing information
There are 3 primary types of missing data.
Missing completely at random (MCAR) information are randomly distributed across the variable and unrelated to other variables.
Missing at random (MAR) data are not randomly distributed simply they are deemed for by other observed variables.
Missing non at random (MNAR) information systematically differ from the observed values.
You tin can utilize the qt() part to find the critical value of t in R. The part gives the critical value of t for the ane-tailed test. If you desire the critical value of t for a 2-tailed examination, separate the significance level by two.
qt(p = .025, df = 29)
You lot tin apply the T.INV() office to find the critical value of t for one-tailed tests in Excel, and you tin utilize the T.INV.2T() function for ii-tailed tests.
=T.INV.2T(0.05,29)
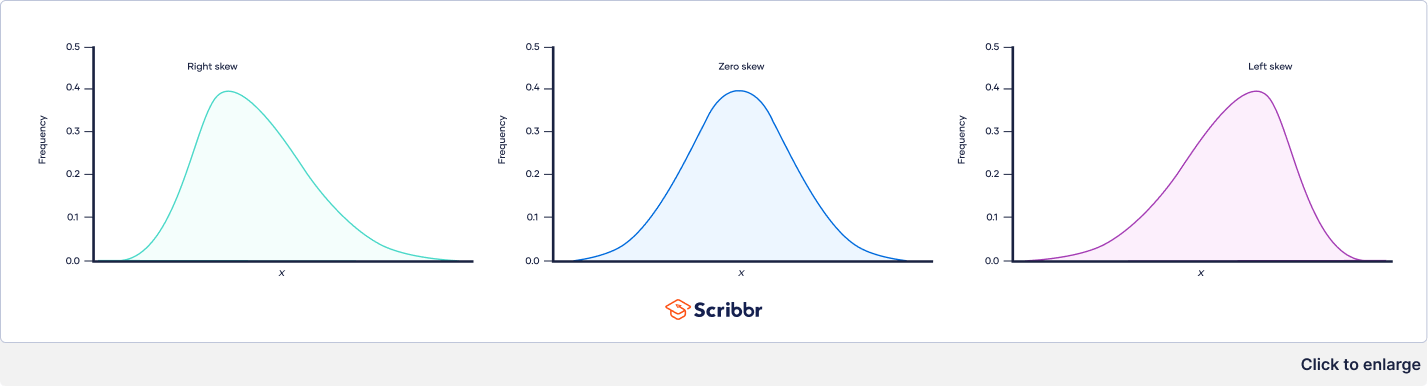
The three types of skewness are:
- Right skew (also chosen positive skew). A right-skewed distribution is longer on the correct side of its elevation than on its left.
- Left skew (also called negative skew). A left-skewed distribution is longer on the left side of its height than on its right.
- Zero skew. it is symmetrical and its left and right sides are mirror images.
Yous can use the QUARTILE() part to find quartiles in Excel. If your data is in column A, so click any blank prison cell and blazon "=QUARTILE(A:A,1)" for the starting time quartile, "=QUARTILE(A:A,2)" for the second quartile, and "=QUARTILE(A:A,3)" for the third quartile.
You can utilise the quantile() role to notice quartiles in R. If your data is chosen "data", and so "quantile(data, prob=c(.25,.5,.75), blazon=1)" will render the three quartiles.
Chi-square goodness of fit tests are often used in genetics. One common application is to check if two genes are linked (i.east., if the assortment is independent). When genes are linked, the allele inherited for one gene affects the allele inherited for another gene.
Suppose that you want to know if the genes for pea texture (R = round, r = wrinkled) and color (Y = yellow, y = green) are linked. Yous perform a dihybrid cross betwixt two heterozygous (RY / ry) pea plants. The hypotheses you're testing with your experiment are:
- Naught hypothesis (H 0): The population of offspring have an equal probability of inheriting all possible genotypic combinations.
- This would propose that the genes are unlinked.
- Alternative hypothesis (H a): The population of offspring do non have an equal probability of inheriting all possible genotypic combinations.
- This would suggest that the genes are linked.
You detect 100 peas:
- 78 round and yellow peas
- 6 round and greenish peas
- 4 wrinkled and yellow peas
- 12 wrinkled and green peas
Step ane: Calculate the expected frequencies
To calculate the expected values, you tin can make a Punnett square. If the two genes are unlinked, the probability of each genotypic combination is equal.
| RY | ry | Ry | rY | |
| RY | RRYY | RrYy | RRYy | RrYY |
| ry | RrYy | rryy | Rryy | rrYy |
| Ry | RRYy | Rryy | RRyy | RrYy |
| rY | RrYY | rrYy | RrYy | rrYY |
The expected phenotypic ratios are therefore 9 round and yellow: 3 circular and dark-green: 3 wrinkled and yellow: one wrinkled and green.
From this, you lot can calculate the expected phenotypic frequencies for 100 peas:
| Phenotype | Observed | Expected |
| Round and yellow | 78 | 100 * (9/sixteen) = 56.25 |
| Circular and green | six | 100 * (three/16) = 18.75 |
| Wrinkled and yellow | 4 | 100 * (three/16) = 18.75 |
| Wrinkled and green | 12 | 100 * (i/16) = vi.21 |
Step ii: Summate chi-square
| Phenotype | Observed | Expected | O − E | ( O − Eastward ) 2 | ( O − Due east ) 2 / E |
| Circular and yellow | 78 | 56.25 | 21.75 | 473.06 | eight.41 |
| Circular and green | vi | 18.75 | −12.75 | 162.56 | viii.67 |
| Wrinkled and yellow | 4 | 18.75 | −14.75 | 217.56 | 11.6 |
| Wrinkled and greenish | 12 | 6.21 | five.79 | 33.52 | five.4 |
Χtwo = 8.41 + 8.67 + 11.6 + 5.4 = 34.08
Pace 3: Find the critical chi-square value
Since there are four groups (round and yellow, circular and greenish, wrinkled and xanthous, wrinkled and light-green), in that location are three degrees of freedom.
For a test of significance at α = .05 and df = 3, the Χ2 critical value is vii.82.
Stride 4: Compare the chi-square value to the disquisitional value
Χtwo = 34.08
Critical value = 7.82
The Χ2 value is greater than the critical value.
Step 5: Decide whether the turn down the null hypothesis
The Χ2 value is greater than the disquisitional value, and then we pass up the zip hypothesis that the population of offspring have an equal probability of inheriting all possible genotypic combinations. There is a significant divergence between the observed and expected genotypic frequencies (p < .05).
The data supports the alternative hypothesis that the offspring do non have an equal probability of inheriting all possible genotypic combinations, which suggests that the genes are linked
Which Measure Of Central Tendency Is Most Often Used When The Data Has Extreme Scores?,
Source: https://www.scribbr.com/frequently-asked-questions/whats-the-best-measure-of-central-tendency-to-use/#:~:text=The%20median%20is%20the%20most,distributions%20or%20distributions%20with%20outliers.
Posted by: hoangroustich1959.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Measure Of Central Tendency Is Most Often Used When The Data Has Extreme Scores?"
Post a Comment